HTML5 custom data attributes, denoted as data-*, offer a powerful way to embed custom data within HTML elements without affecting their presentation or behavior.
Why Use Custom Data Attributes?
Custom Data Attributes provide a clean method to store extra information directly in the markup.
Let’s see how they help developers create more interactive and maintainable applications.
Store Extra Information
Custom data attributes allow developers to add custom information by adding metadata within HTML tags. This approach keeps the HTML semantic and organized, making it easier to maintain.
For instance, you can store user IDs, roles, or any other relevant information:

Simplify JavaScript Interactions
Accessing and handling custom data attributes with JavaScript is straightforward using the dataset property.
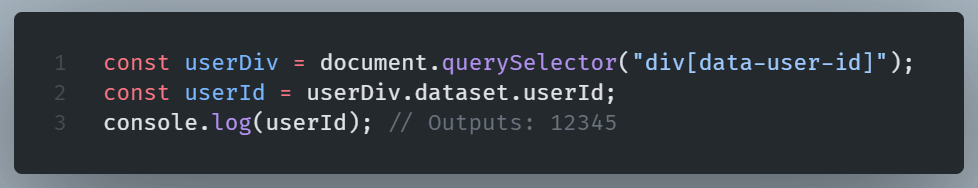
This method simplifies accessing and modifying custom data, keeping your JavaScript clean.
Better CSS Styling
While CSS doesn’t have direct access to data attributes, you can use attribute selectors to apply styles based on their values:

This technique enables dynamic styling without extra classes or IDs.
Practical Example: Interactive Button
Let’s see a practical example of using custom data attributes in CSS, Javascript and HTML.
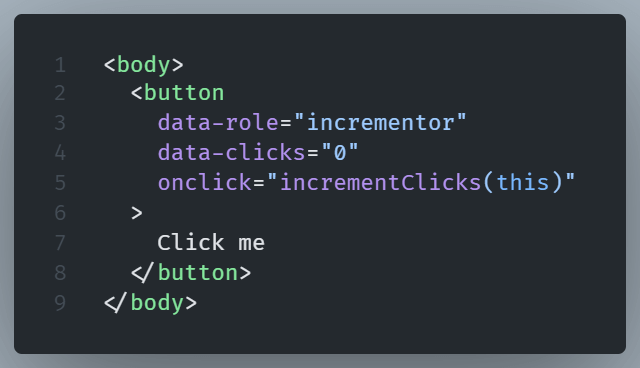
Consider a button that counts its clicks.
HTML:
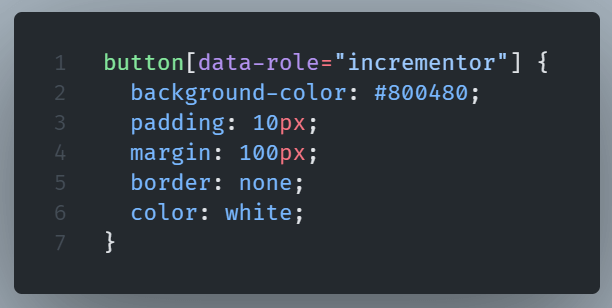
CSS:
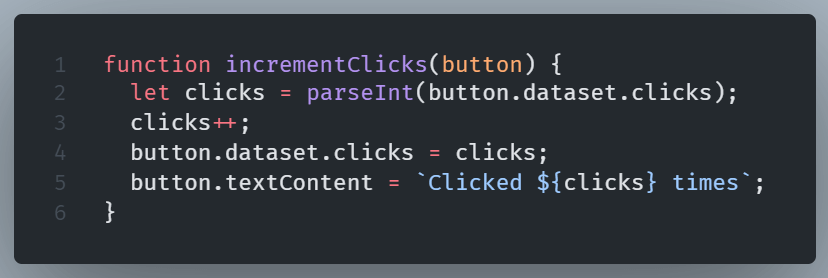
JavaScript:
Result:

Best Practices for Using HTML5 Custom Data Attributes
1. Use Descriptive and Consistent Naming Conventions
Choose meaningful names for your data attributes to make your code more readable and maintainable.
For example:

This approach improves code understanding by clearly defining the purpose of each attribute.
2. Avoid Storing Sensitive or Large Data
Avoid using custom data attributes to store sensitive information.
Additionally, refrain from storing large datasets or complex JSON objects, as this can bloat your HTML and negatively impact performance.
3. Maintain Semantic HTML Structure
Using data attributes shouldn’t break the semantic structure of your HTML. They should supplement, not replace, standard HTML elements and attributes.
For example:
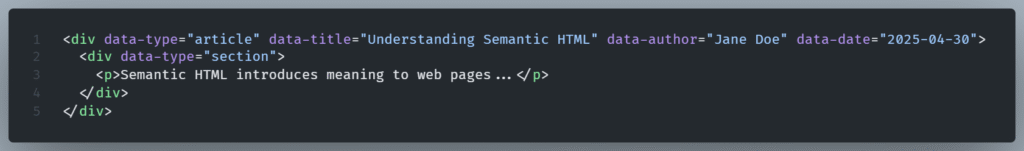
Generally try to avoid:
- Over-dependance on <div> elements, which lack semantic meaning.
- Use of data-type (data-type=”article”) to mimic semantic tags, which can confuse assistive technologies and hinder SEO.
- Embedding critical content information within data attributes rather than visible, structured HTML elements. More specifically instead of using a heading it depends on data-title. This way it confuses the document’s structure, making it harder for screen readers and search engines to parse the content effectively.
Following these best practices will help you use HTML5 custom data attributes to build better web apps.
Custom data attributes offer a clean way to pass information between HTML and JavaScript, enhancing user experience without compromising code structure.