We’ve seen how the search engines employ automated programs, known as “crawlers” or “spiders,” to scrutinize the internet for fresh or revised web pages.
Once a page is crawled, the search engine processes and stores its information in a massive database (index).
Search engines use this database to pick indexed web pages for search results.
I like to use the example of a library with the index being the library and the Search Engine being the librarian. When a member searches for a topic (search query), the librarian (Google) suggests a handful of books (search results) that relate to that topic.
A Search Engine can’t access every site on the internet.
Even Google, despite its enormous size, can only display indexed websites in search results. If Google doesn’t index a website, it’ll be absent from search results and have a zero ranking.
When that happens, we get the “Crawled — currently not indexed” error message in Google Search Console.
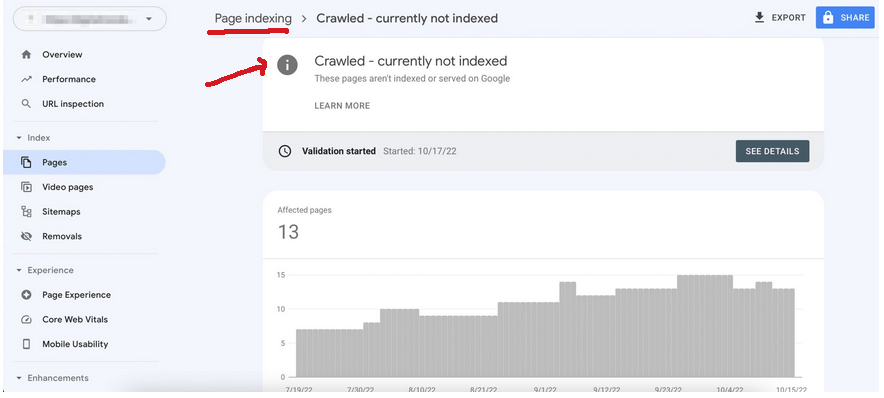
That message means, the Search Engine sees the page without saving the data, which prevents it from being ranked.
How to get a webpage indexed?
There are several reasons why a Search Engine might not index a site.
The following are some of the factors affecting Google’s indexing process:
1. No Internal Links
Google might miss a page on a website that isn’t linked to anywhere else and even if a crawler end up visiting it, it might not be indexed.
The solution to this is to link to the page from other relevant pages on the same website.
Another fix is to add the page to the main navigation, sitemap, or footer.
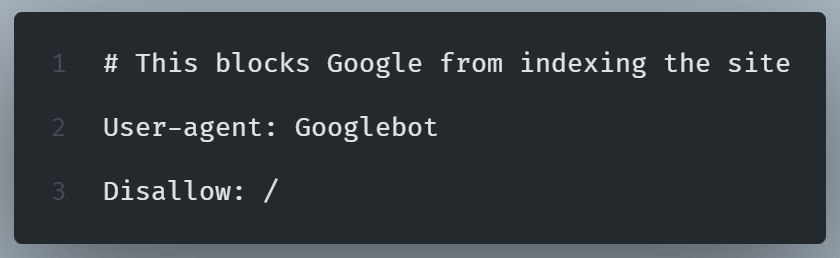
2. Robots.txt Blocking Google
If the robots.txt file blocks search engines, Google won’t crawl the page.
We can check robots.txt at website.com/robots.txt.
To fix this, we must remove disallow rules if they block important pages:
Note: If the webpage was crawled earlier (before the block) or has internal links, or/and outbound links, it will be remain indexed despite the disallow directive in robots.txt file.
The URL will show up in search results, however, it will lack a description.
3. Meta Tag “Noindex”
If a webpage has a noindex meta name="robots" attribute , Google will ignore it.
In order to fix this we can check the page’s HTML HEAD:
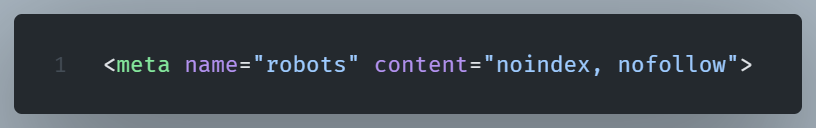
If we want the page to be indexed we can remove the noindex.
NOTE: Check Google Search Console → URL Inspection Tool to confirm.
4. Page is Slow
Reduced indexing and crawl rates can result from slow-loading websites.
To fix this we can use the Google PageSpeed Insights to check speed.
In order to improve speed, we can take measures like optimize images, enable caching, and use a CDN.
5. Duplicate Content
If Google sees the content as a duplicate, it may ignore it.
How to remedy duplicate content issue:
Refrain from publishing very similar content.
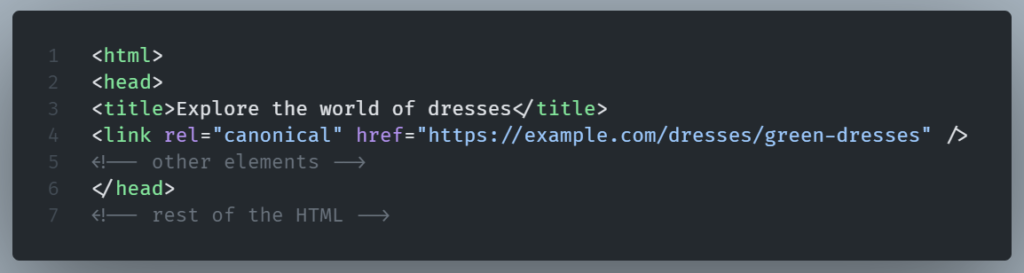
In order to remedy duplicate content issues, we can set a canonical tag (rel="canonical") to point to the original version.
The canonical URL, specified by the rel=”canonical” attribute, signals to search engines which URL is the primary version of a page.
6. Google Hasn’t Re-crawled the Site Yet
If we’ve recently added or made changes to a page on a webpage, we can request that Google re-index that page using by using the URL Inspection tool.
7. Manual Google Penalty
Google may penalize sites breaching its Search Essentials guidelines with manual actions.
If a website has violated these guidelines (spam, keyword stuffing, etc.), it may be manually de-indexed.
What a website owner can do is fix the violations, as they are messaged in Google Search Console, and then submitting a reconsideration request.
How to Check If Google Has Indexed a Page?
To check if a webpage is indexed by Google we can check with the Google URL Inspection Tool.
This process is similar with other search engines like bing which have its own URL inspection tool.