An API, abbreviation for Application Programming Interface, is a set of rules that lets one piece of software talk to another. In the case of web development, a client (browser) and a server.
An API acts as a messenger, carrying requests and returning responses.
It resembles a menu in a restaurant. The menu lists what you can ask for. The kitchen (server) can produce certain dishes. You (the client) don’t need to know how the kitchen works. You just place an order, and the kitchen delivers the result. An API works the same way:
- You send a request.
- The server receives it, does its work, and sends back a response.
APIs come in many forms, but the goal is always the same: make communication between systems easier and more predictable. A browser, a mobile app, a server, or even another API can use them to request data or trigger actions.
For example:
- A weather app uses an API to get today’s forecast.
- A website uses an API to load user information.
- A payment system uses an API to process transactions securely.
You just interact with the API’s “menu” without seeing the internal code, the database, or the logic behind the scenes. The API defines what you are allowed to request and how you must ask.
In short, an API is a bridge that lets software communicate in a structured and consistent way.
So, What is a REST API?
REST stands for Representational State Transfer. It’s an architectural style for designing networked applications that is used in web APIs.
In a REST system, information is shared between a client (like your browser or mobile app) and a server (where the data lives). They communicate through HTTP, the same protocol that powers web pages.
It is like a conversation:
- The client asks the server for something (a resource).
- The server responds with that resource in a format like JSON or XML.
The Main Idea: Data and Methods
In REST, everything is treated as a piece of data you can access or modify. For example:
/usersmight represent all users./users/1might represent a single user.
To interact with these data, REST uses standard HTTP methods:
- GET → Retrieve data
- POST → Create new data
- PUT → Update existing data
- DELETE → Remove data
These methods keep REST APIs simple and predictable since the same patterns work across different systems.
Why REST Became So Popular
REST APIs are easy to understand because they rely on familiar web standards. You can test them using a browser or tools like Postman or curl.
They’re also stateless. Every request contains all the information the server needs to understand it. This makes systems easier to scale and maintain over time.
Here’s how a client might use a REST API to get information about a user:
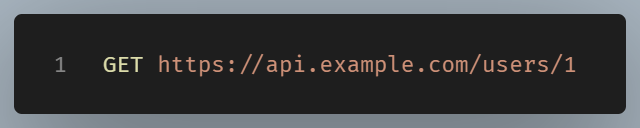
And the server could respond with:
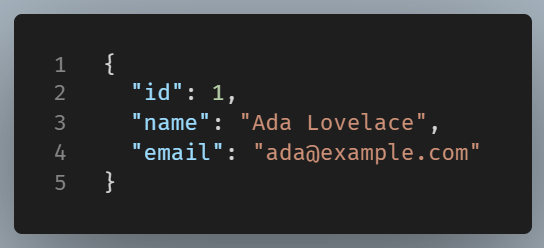
If you wanted to add a new user, you’d use POST instead, sending data in your request.
Wrapping Up
We talked about what an API is and explored REST, emphasizing how it helps in communicating with a server to create, read, update, and delete the data stored there.
When you fully grasp the idea, working with or constructing REST APIs feels like a reasonable next step in the modern web development world.