Set operations let you combine, compare, and modify sets. These operations are based on basic mathematical ideas, but you do not need a math background to use them since Python does all the work under the hood.
The most common operations answer simple questions:
- Which items appear in both sets?
- Which items appear in either set?
- Which items appear in one set but not the other?
Intersection
The intersection operator (&) finds items shared by both sets.
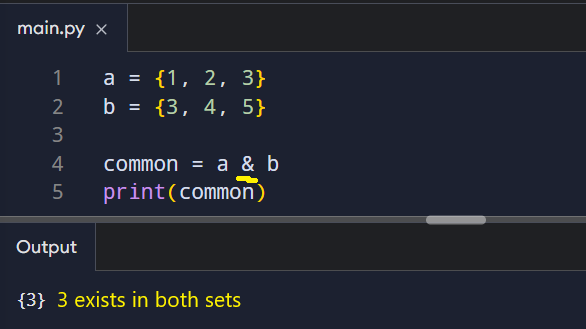
This is useful when you want to detect overlap. For example, shared permissions or matching IDs.
Union
The union operator (|) merges all unique items from both sets.
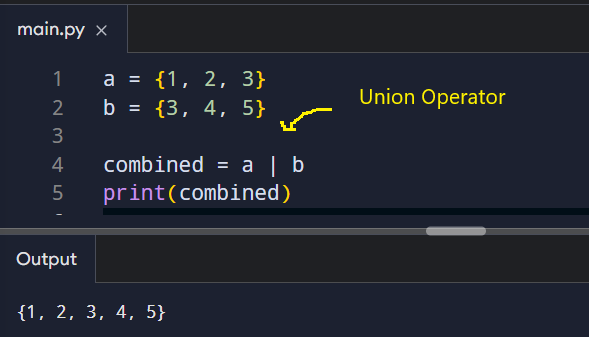
This is helpful when merging data sources while avoiding duplicates.
Difference
The difference operator (-) finds items that exist in one set but not the other.
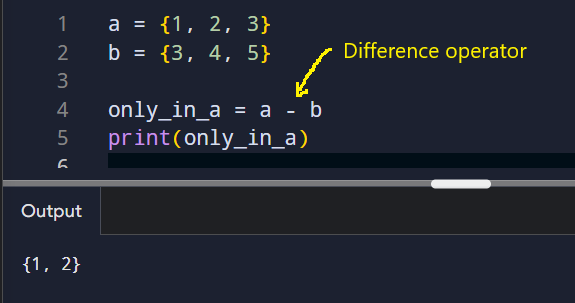
This answers questions like what remains after removing known items.
Symmetric Difference
The symmetric difference operator (^) finds items that appear in only one set, but not both.
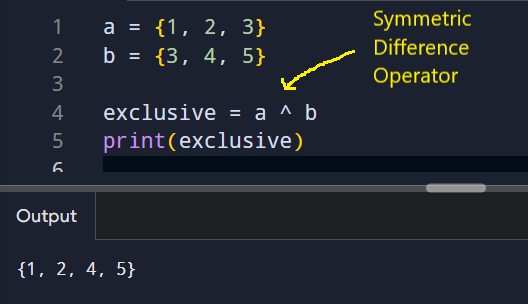
This is useful when you want to find mismatches or differences between two collections.
Checking Relationships Between Sets
Sets can also be compared logically.
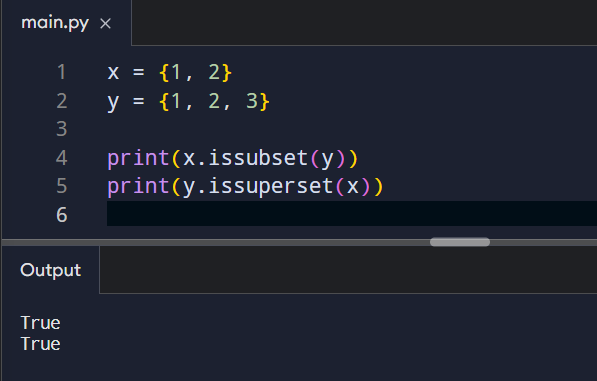
This helps when validating whether one group is fully contained inside another.
Wrapping Up
Set operations deal with how groups relate. They remove the need for loops and conditionals, since Python does the heavy lifting under the hood. The code stays short, and readable.