In Python, operators are symbols that perform operations on variables and their values.
Let’s see a few examples.
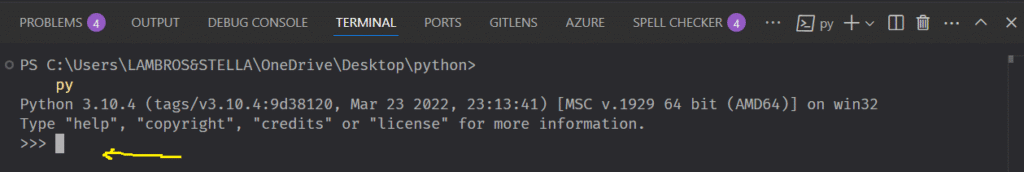
Begin by initiating a REPL.
In Window you type py and press enter. In Mac and Linux you would type python3.
The Python REPL is now running.
The assignment operator
We have seen examples of assignment operators in previous posts.
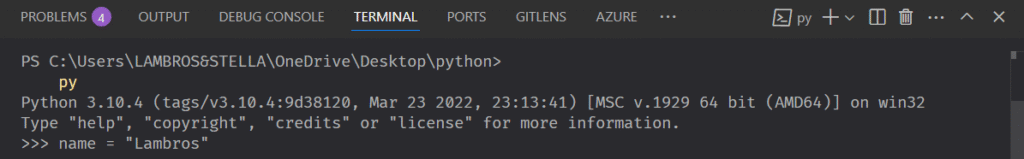
The assignment operator is just the equal sign =.
I typed name equals and after I did that I assigned the value ‘Lambros‘ to the name variable.
Now I can get that value back by typing that variable in the REPL.
Arithmetic operators
Arithmetic operators are known from math.
First we have the addition.

So we can use Python just like a calculator. We add two numbers together.
We can also do subtraction.

And also multiplication.

And lastly division.

In Python there is a second type of division. The floor division. This type of division, contrary to the typical one that can return a decimal number, returns a rounded down number.
The Floor Division uses two slashes as an operator.

If we want to round a division up, we can use the round function.

We see that the round function returns different results than the floor division operator.
But what if we want the remainder of this division?
We can use the percentage sigh %. We call it the remainder operator and it returns exactly that. The remainder of a division.

We can also use exponents. If want to calculate three to the power of two we can do that by using two asterisks.

Combining Assignment operator with arithmetic operators
We can combine assignment and arithmetic operators when using variables.
For example we can combine the assignment operator with the plus sign.

This is the equivalent of
number = number + 1Likewise we can take the “number” variable and use the combination of the assignment operator with the minus operator or any other arithmetic operator for that matter.
number -= 3
Concatenation
We can use the plus operator for concatenating two different strings.

We add two different strings together and one string is returned that has concatenated the two strings.
Comparison Operators
If we want to check if one number is equal to another we use the double equals operator.
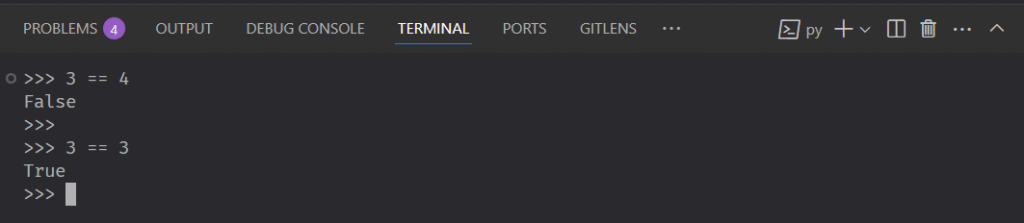
Since the two numbers are obviously not equal the response is False.
If the two numbers were equals it would be True.
Since the double equal operator can return only False or True is called a Boolean operator.
Another Boolean operator is the Not-Equal operator !=.
If we want to check say 3 != 3 it will return False.
If we check 3 != 4 it will return True.
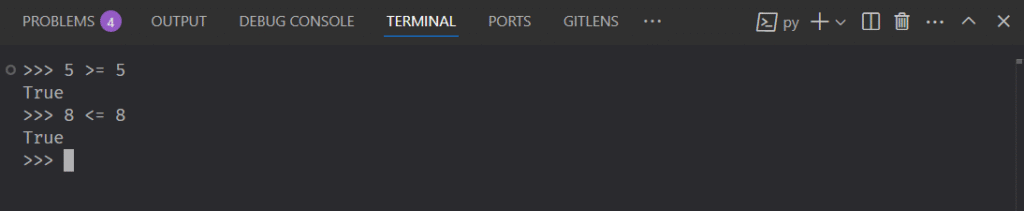
Other Boolean operators are the ‘Greater Than‘ > and ‘Greater Less‘ < operators.

There are also the ‘Greater Than and Equal‘ and ‘Greater Less and Equal‘ operators.