In Python, True and False are the foundation for important decisions:
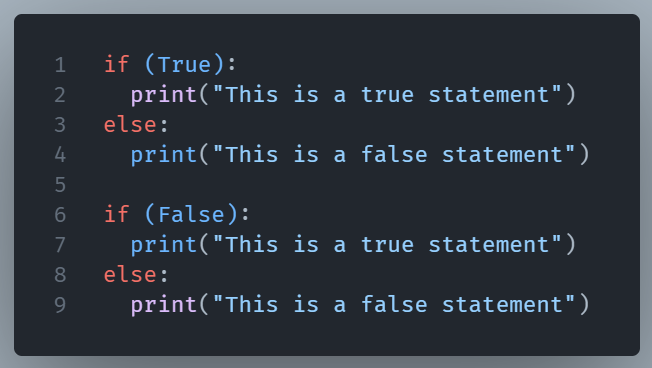
These are Booleans. They are named after mathematician George Boole and they’re the foundation of how Python (and many other languages) think.
While numbers calculate and strings store text, Booleans control logic. They’re behind if statements, loops, and conditions.
The bool type inherits its properties from the int type!
This is intentional in Python and not a bug from design.
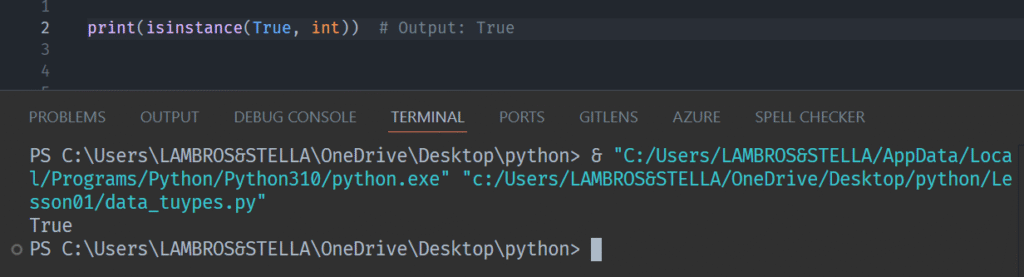
The bool type actually inherits from int. That means True and False are essentially integers under the hood:
Trueis equal to 1Falseis equal to 0
So you can do things like:
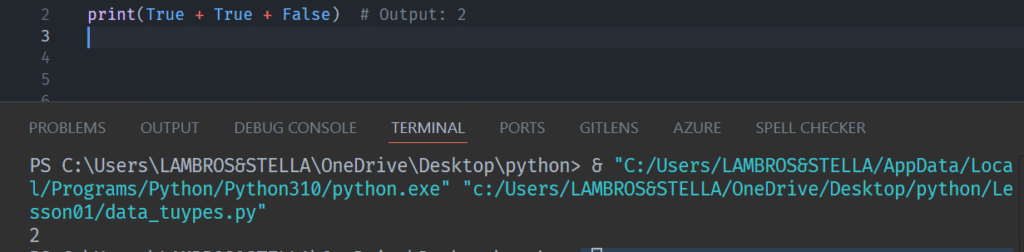
and also:
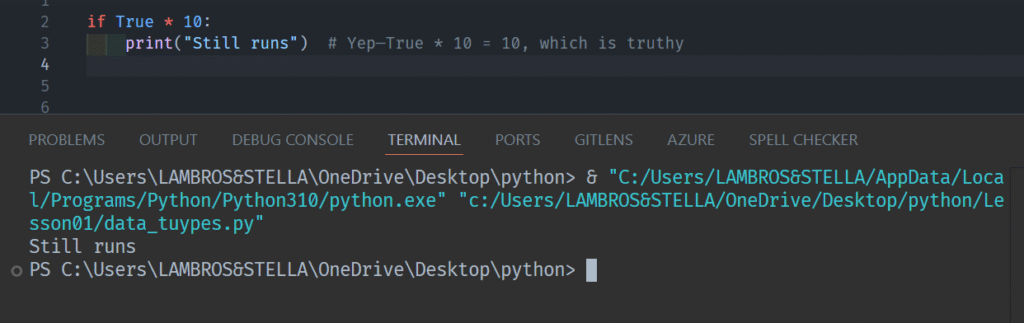
This behaviour is unique in Python!
Most mainstream languages treat Booleans as strictly separate from integers.
More specifically, to the languages that we are interested in here (JS, PHP):
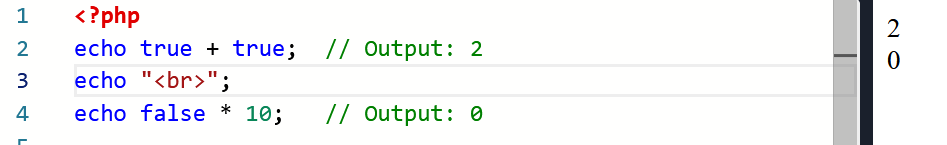
In PHP: Unlike Python, true and false in PHP are not a subclass of any numeric type. They’re part of their own distinct type: boolean.
When used in numeric contexts, PHP will coerce Booleans into integers.
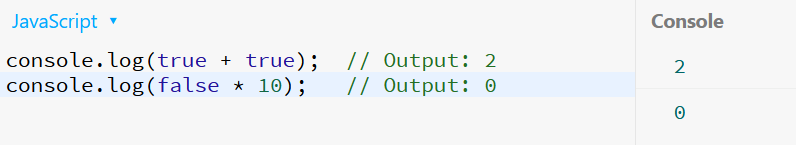
In JavaScript: Booleans get coerced into 1 or 0 in numeric contexts, but they aren’t subclasses of Number.
Python’s twist is that it formally made bool a subclass of int. This means Booleans are integers—with all the behavior you’d expect from an object-oriented hierarchy.
To put it simply, the difference is that Python formally binds True and False to int. PHP just coerces them when needed, kind of like JavaScript.
How Python Determines True or False
In many cases, Python can determine True or False without your explicit input.
Here’s how Python treats some values:
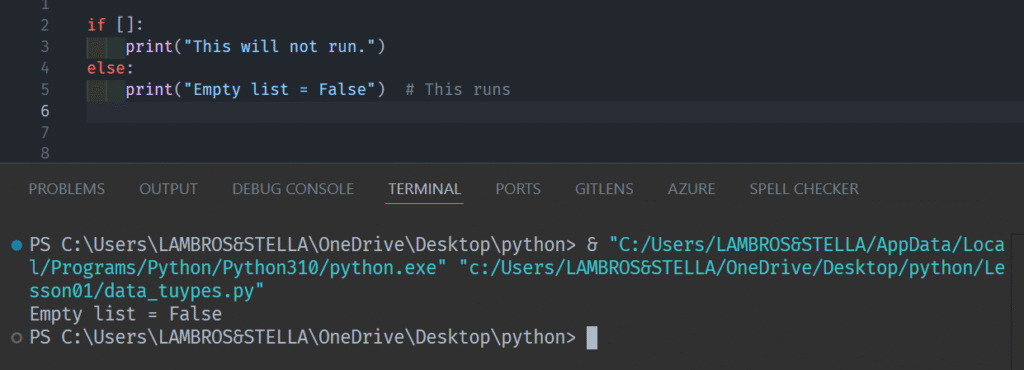
- Falsy: 0, 0.0, “” (empty string), [] (empty list), {} (empty dict), None
- Truthy: Anything else
Where You’ll Use Booleans
Whenever you’re checking if something is or isn’t the case, you’re dealing with Booleans.
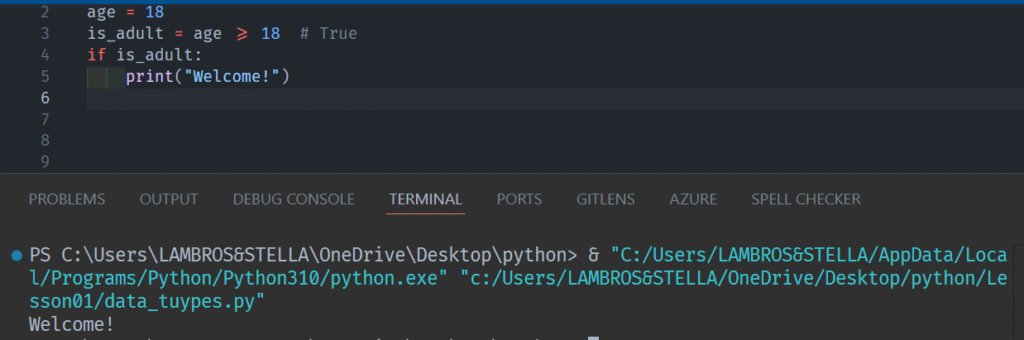
You’ll use Booleans to:
- Check conditions (
if,while) - Compare values (
==,!=,<,>=) - Combine conditions using
and,or, andnot
Conclution
The Boolean type powers every decision in your code. And once you start writing more logic, especially in user input, game rules, or web requests, you’ll appreciate just how deeply these two little values run.