In HTML, you can include sound into your code, using the audio element.
Compatible with audio element, are popular audio formats like mp3, WAV, and OGG.

Running this example will show nothing on the page. But, if you check the page using the developer tools, you can see the audio element is there.

In order to view the audio player, you just include the controls attribute.

The controls attribute allows users to adjust volume, pause, and resume audio playback.

If you omit the controls attribute, no controls will be shown.
Besides the src and controls attributes, the audio element has other attributes enhancing its functionality.
One of them is the loop attribute which makes the audio play repeatedly.
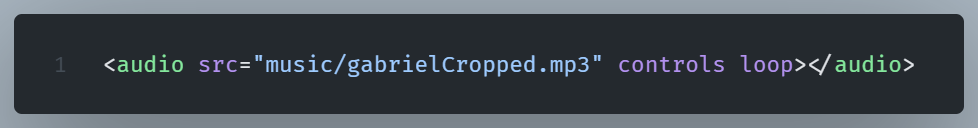
With this attribute,the song currently playing will restart automatically upon completion.
Another attribute we can use is the muted attribute.
Including the muted attribute in the audio element will start the audio in a muted state.
That means that when you start the song in the browser, you’ll not hear anything unless you click on the volume icon.
Let’s see an example of using the muted attribute:

Different browsers support different audio file types.
This is handled by placing source elements inside the audio element; the browser will automatically use the first compatible one.
Below is an example of using multiple source elements for an audio element:

The browser tries the ogg format first; if that fails, it falls back to the next audio type.