In programming, we instruct computers to do things, and we call these instructions programs.
We can write programs using different programming languages, the same way we can communicate with other humans using different human languages.
Each language consists of rules that dictate how to use data, and each data has a type.
The operations that the computer performs are based on these types.
Various data types require different memory allocation and support different operations.
PHP has its own set of data types. We are going to get into them in this post.
PHP is a loosely typed language
There are two kinds of programming languages, loosely typed, and strongly typed, with PHP falling into the former category.
Before delving into data types, let’s make this distinction clearer.
In programming, we can store data for later use in computer memory locations called variables.
These variables are essentially containers of data types.
We give these containers a name in order to manipulate them in our programs.
In PHP, variable names are prefixed with a dollar sign, and they must start with a letter or an underscore.
…varNames
They can include also numbers but they can’t start with one of them.
…varNames2
NOTE: In PHP, variables are case sensitive.
So capital letters matter.
We have declared the variable $name already, but not a variable named $Name.
…varName3
Loosely typed languages do not require variables to be defined
Regarding the previous example, we stored data into variables without explicitly define the type of that data.
We can do this in PHP because it is a loosely typed language.
If we have written these variables in a strongly typed language, we would have to define the type of the data in that variables.
This is an example in C# which is a strongly typed language:
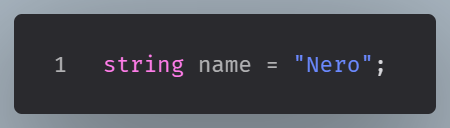
Here, we explicitly define that the name variable is a string, and we cannot put any other type in that variable.
Data Types
PHP supports the following data types:
- Integer
- Float (floating point numbers)
- String
- Boolean
- NULL
- Array
- Object
- Resource
Let’s dive deep into them:
Integer
An integer is a non-decimal number between -2,147,483,648 and 2,147,483,647.
For a data type to be classified as Integer, it must have at least one digit, and must not have a decimal point.
Integers can be positive or negative.
Regarding indegers in CS, we note that:
We use the decimal number system for counting and measuring, but computers operate using a binary number system, with transistors functioning in two states – on and off.
In computing, we also use hexadecimal and octal number systems in order to represent binary numbers more efficiently.
We can define PHP integers as: decimal (base 10), hexadecimal (base 16), octal (base 8), or binary (base 2) notation.
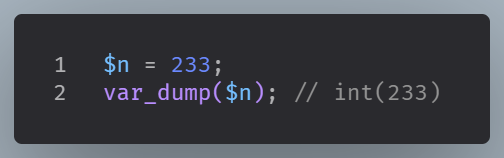
In the following example, $n is an integer. The PHP var_dump() function returns the data type and value: